Stainless steel can be affected by stress corrosion cracking (SCC) in Chloride and sulphide containing environment at elevated temperatures. Conventional austenitic stainless steel is particularly susceptible to stress corrosion cracking while duplex stainless steels are less susceptible to this type of corrosion.
In many practical applications, a typical example of Chloride Stress Corrosion Cracking (CSCC) is observed in plate type heat exchanger consists of ASTM A240 TP316 operating in Hot water/ Crude service.
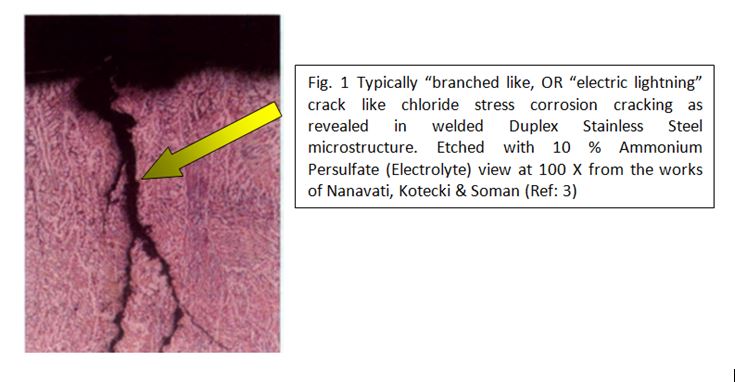
They often failed due to chloride stress corrosion cracking as revealed by microstructure bearing typically “branched like, OR “electric lightning” crack (Ref 1-3). The combination of high temperature, high chloride content and the cold worked plate Type 316 material, becomes highly susceptible to Chloride Stress Corrosion Cracking (CSCC) leading to failure. However, as with many materials, the duplex stainless steels may be susceptible to stress corrosion cracking under high temperature, chloride-containing environments, or when conditions support hydrogen-induced cracking (HIC) as shown in Fig. 1 (Ref: 3)
Ref: 2
Ref: 3
P. K. Nanavati & D. J. Kotecki & Sanjay N. Soman (2019), Effect of weld metal ferrite content on mechanical properties and stress corrosion cracking resistance in 22 Cr 5 Ni duplex stainless steel, Welding in the World, https://doi.org/10.1007/s40194-019-00708-1. Published online 13 February 2019. Print:- Welding in the World 63 (3), 793-805